论文学习(1):Generalized Linear Mixed Models
近期在学习广义线性混合效应模型,看了一篇文章,谷歌学术引用8k, Generalized Linear Mixed Models: A Practical Guide for Ecology and Evolution (Bolker, Benjamin M., et al. 2009)下载
摘要
固定效应和随机效应,可粗略将随机效应理解为分组效应。一组数据内存在组间差距,典型的比如一堆学生调查数据其中来自多个班级,这里班级即考虑为一个随机效应,因为不同班级本身存在一个偏差/截距因此不能直接进行建模。
大意:GLMMs在生态领域应用十分广泛,但是对于模型的使用、拟合及参数估计等还是存在一些问题,本文的工作是回顾了模型的使用,讨论了GLMM中的参数估计和模型推断,并总结了一份数据分析步骤的“最佳的实践”。
How should ecologists and evolutionary biologists analyze nonnormal data that involve random effects? Nonnormal data such as counts or proportions(因变量为包含随机效应的非正常数据比如频次,百分比等) often defy classical statistical procedures. Generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs) provide a more flexible approach for analyzing nonnormal data when random effects are present. The explosion of research on GLMMs in the last decade has generated considerable uncertainty for practitioners in ecology and evolution. Despite the availability of accurate techniques for estimating GLMM parameters in simple cases, complex GLMMs are challenging to fit and statistical inference such as hypothesis testing remains difficult. We review the use (and misuse) of GLMMs in ecology and evolution, discuss estimation and inference and summarize ‘best-practice’ data analysis procedures for scientists facing this challenge.
内容
自行阅读,本文的核心内容都通过图表的形式呈现了,很友好,尤其是一开始的统计相关的一些知识总结。
概念表
一些统计学的概念可能需要进一步学习和在实践中逐渐体会:Bayesian statistics, Bias, Block random effects, Continuous random effects, Crossed random effects, Exponential family,……
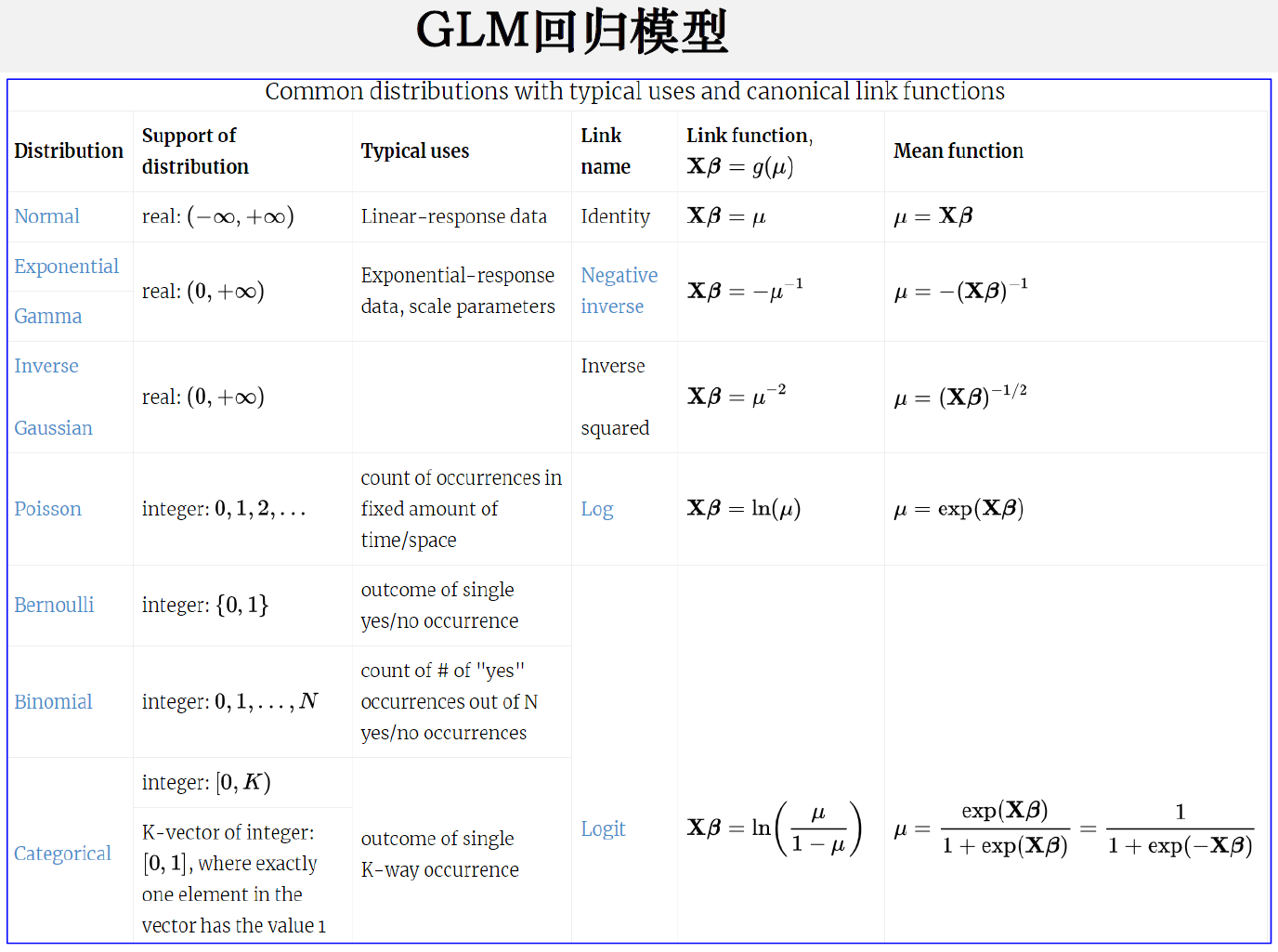
统计模型的选择和处理依赖于因变量的类型,关于GLM回归模型延伸一下,针对不同变量类型采取的不同变换,借用老师上课时候的一张PPT:
模型参数估计
步骤及方法详情,具体可阅读论文,以下图文均来自论文
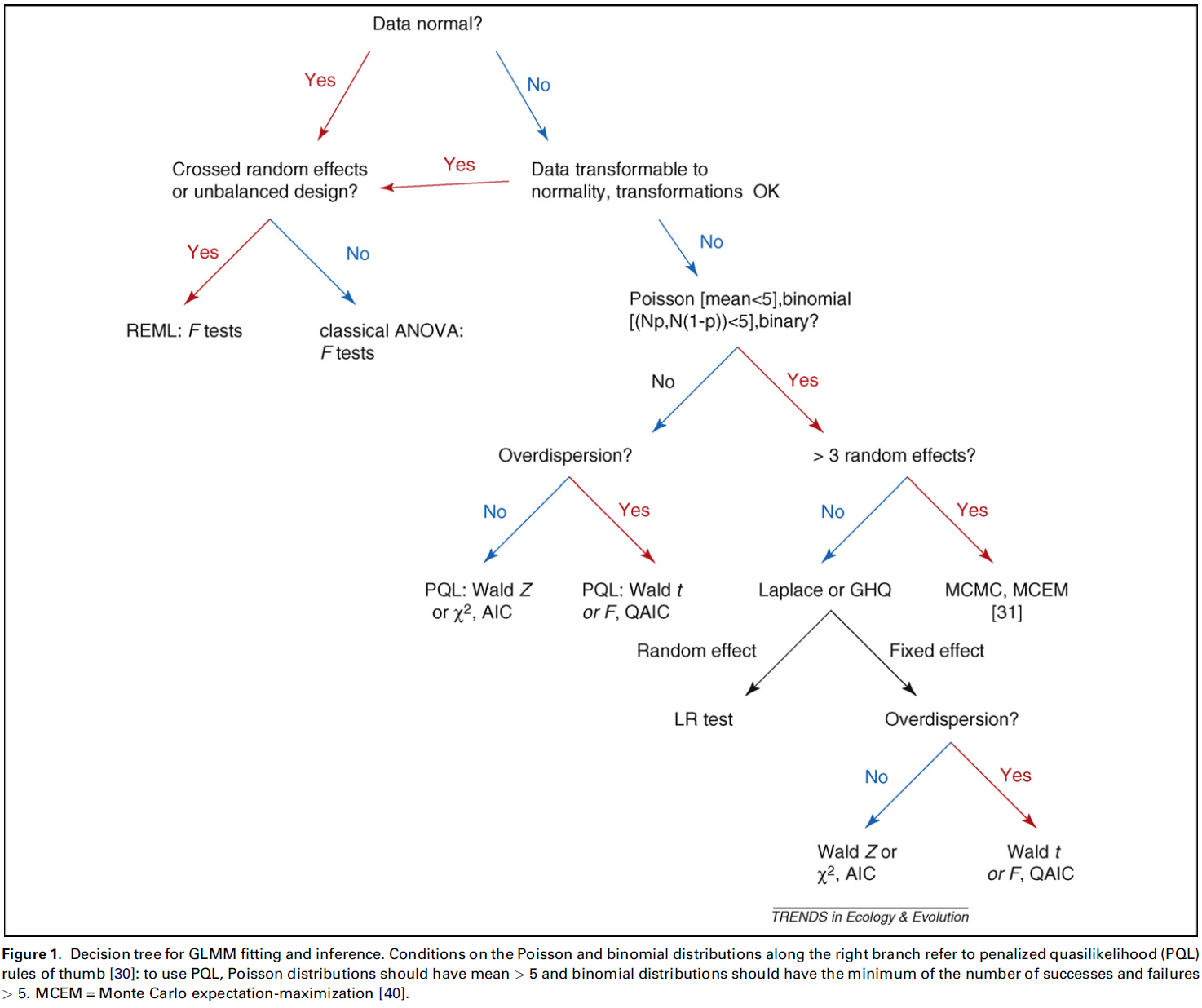
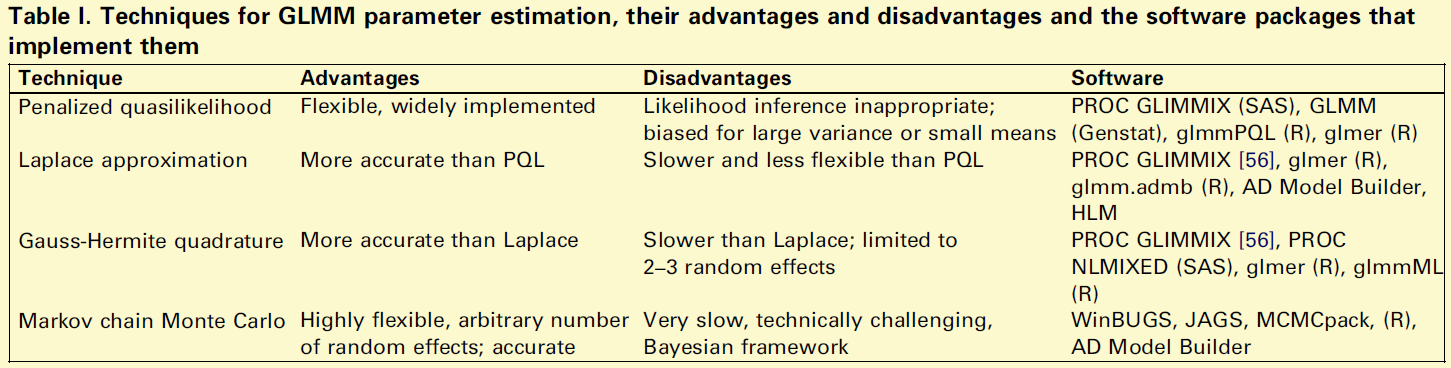
模型推断方法
在估计了GLMMs的参数值后,下一步是统计推断:即通过检查估计值及其置信区间、测试假设、选择最佳模型和评估模型间的拟合度差异,从数据中得出统计和生物学结论。本文讨论三种一般的推理类型:假设检验、模型比较和贝叶斯方法。
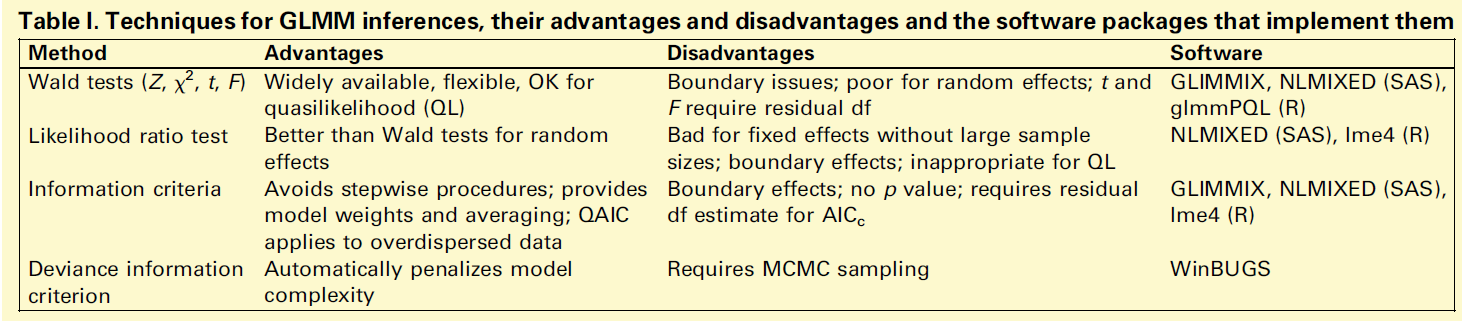
完整建模指南
具体情况具体分析,初步实践可以看一下这个教程,我觉得写的建模思路比较完整
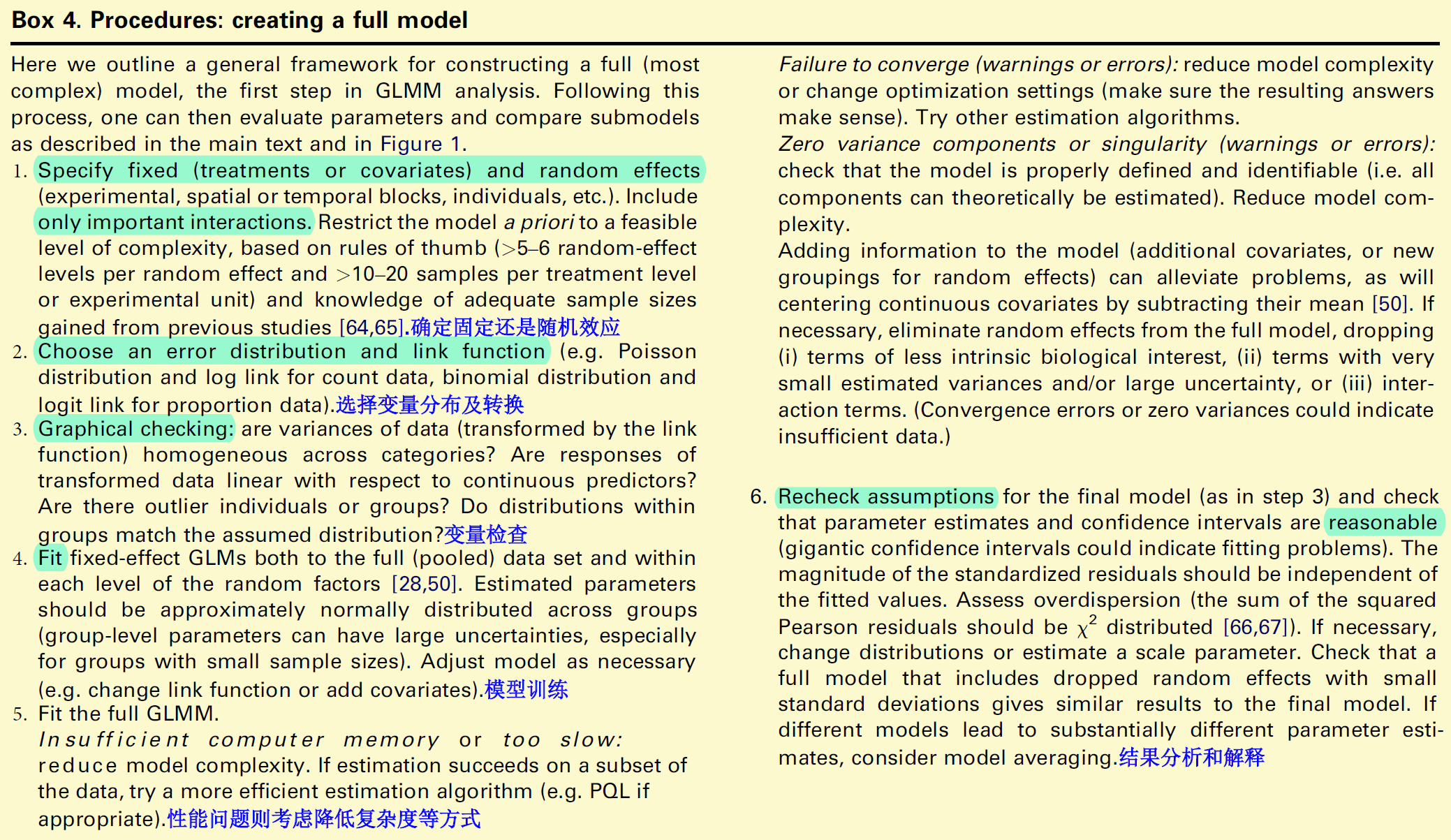
参考
Bolker另一篇高引用文章(引用52498),2015-Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4是R语言lme4包的介绍和模型拟合,略长,还没来及看
Bolker, Benjamin M., et al. "Generalized linear mixed models: a practical guide for ecology and evolution." Trends in ecology & evolution 24.3 (2009): 127-135.
Bates, D., Mächler, M., Bolker, B., & Walker, S. (2015). Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67(1), 1–48. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v067.i01